Ⅰ. Introduction
Ⅱ. Analyzing Methods
1. Beneficial points on analyzing through Game Theory
2. Explanations of games used to analyze
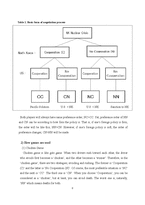
Ⅲ. The First & Second North Korean Nuclear Crisis
1. The First Nuclear Crisis – chicken game
2. The Second Nuclear Crisis – prisoner’s dilemma
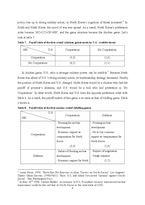
Ⅳ. The Third North Korean Nuclear Crisis
1. Analysis through understanding intuitively
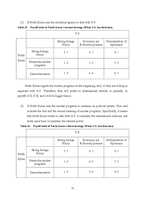
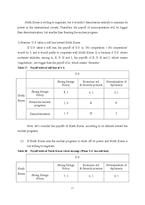
2. Analysis through understanding concrete situations
3. Solution
Ⅴ. Conclusion
References
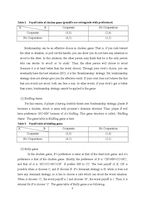
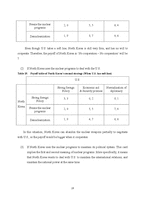
(2) Bluffing Game
For this reason, if player A having credible threat uses brinkmanship strategy, player B becomes a chicken, which is same with prisoner’s dilemma structure. Thus, player B will have preference ‘NC>NN’ because of A’s bluffing. This game structure is called, ‘Bluffing Game’. The game table in Bluffing game is here.
Table 3. Payoff table of bluffing game
A B Cooperate No Cooperation
Cooperate (3,3) (1,4)
No Cooperation (4,2) (2,1)
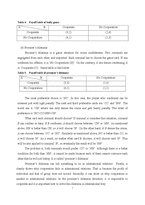
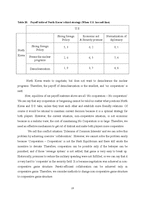
(3) Bully game
In the chicken game, B’s preference is same as that of the dead-lock game, and A’s preference is that of the chicken game. Shortly, the preference of B is ‘CN>NN>CC>NC’, and that of A is ‘NC>CC>NC>CN’. B prefers NN to CC. The best payoff of B, CN is possible when A chooses C, and B chooses N. B’s dominant strategy is N, while A does not have any dominant strategy, so A has to choose a card which can avoid the worst situation. When A chooses ‘C’, the worst payoff is 2 and chooses ‘N’, the worst payoff is 1. Thus, it is rational for B to choose ‘C’. The game table of Bully game is as following.
Kim H, Choi JY. (2002) Uncertainty in Foreign Policy Making: A Bayesian Game Analysis of Korea. Global Economic Review, 31:25-40.
Bae JS. (2004) An Empirical Analysis of the Arms Race Between South and North Korea, Defence and Peace Economics, 15(4): 379-392.
Caplan B. (2000) Rational Irrationality: a Framework for the Neoclassical-Behavioral Debate, Eastern Economic Journal, Vol. 26, No. 2
David C. Kang, 2003, Nuclear North Korea: Debate on Engagement Strategies, New York : Columbia University Press.
Dick K, Emma C. (2010) North Korea: Economic Leverage and Policy Analysis, CRS Report for Congress
Hwang JH, 2006, “Analysis of 1st and 2nd nuclear crisis”, International Policy collection of writings, 46:1, p. 80
Jonathan D. Pollack, 2003, “The United States, North Korea, and the End for the Agreed Framework”, Naval War College Review 56:3, p. 44
Lee HK. (2008) Corresponding Steps and Further Approaches for North Korean Nuclear Solution through Application of Game Theory, Bargaining Theory, and Prospect Theory, The Korean Society for GeoSpatial Information System, Vol. 9, No. 4: 63-87
Mark EM, Mary BN. (2009) Assistance to North Korea, CRS Report for Congress
Morgan PM. (2006) Deterrence and System Management: The Case of North Korea, Conflict Management and Peace Science 23:121-138.
“Nash Bargaining Game.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nash_bargaining_game
“Prisoner’s Dilemma.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prisoner’s_dilemma
Shaun P, Yanis V. (2004) BARGAINING GAMES: Rational agreements, bargaining power and the Social Contract, In: GAME THEORY: A critical text, London, Routledge
Sonni Efron, 2003, “Bush Has His Reasons to Alter Tactics on North Korea”, Los Angeles Times, : Glenn Kessler, 2005/03/22, “Rice: U.S. and Allied Discussed ‘Options’ against North Korea”, The Washington Post.
Wrobel RM. (2007) North Korea after the Nuclear Crisis: the Future of the Economic Reforms, Post-Communist Economies 19(4):484-503.
Wang L., Chakabraty D., Goel G., Vazirani V., and Yu C., "Nash Bargaining Games.", Georgia Tech College of Computing

- 오늘 본 자료가 없습니다.
- 가족복지론] 현재 우리나라에서 시행중인 가족복지정책과 선진복지국가의 가족 복지정책을 비교하고 앞으로 우리나라 가족복지 발전 방향을 제시해 보시오
- 영화 `그대를 사랑합니다`를 통한 노인문제 고찰
- [사회복지현장실습] 사회복지현장실습의 필요성 및 중요성을 정리하고, 실습을 통한 사회복지이론과 실제경험에서 느꼈던 차이점
- 사회복지법이 지금의 현대복지국가의 중요한 법체계로 만들어진 형성과정에 대해서 설명하고 그 과정에서 가장 중요한 영향을 미친 부분에 대해서
- 4주 7차시에서 설문지 조사에 대하여 학습했습니다 설문지 조사는 응답자로 하여금 연구주제와 관련된 질문에 답하게 함으로써 체계적이고 계획적으로 실증적 자료를 수집 분석하는 연구조사방법입니다 설문지 조사의 장 · 단점에 대하여 논하십시오
- 사회화의 의미와 개념을 설명하고 사회화 담당기관의 역할을 설명하고 사회화 교육을 통한 기대효과에 대해 토론하시오
- 건강가정론] 현대 한국 사회의 변화와 함께 나타난 가족의 변화를 설명하고, 이와 함께 등장하고 있는 가족 다양성에 대한 자신의 견해를 논하시오
- 가족상담및가족치료] 가족 의사소통에 있어서 스마트폰 사용의 장점과 단점이 있다면 무엇이 있는지 서술하고, 그에 따른 대처방안들을 본인의 생각과 함께 토론하시오
- 우리나라 맞벌이 가족의 현황과 문제에 대한 해결방안을 설명하시오
- 보육실습의 목적은 학교에서 배운 이론과 지식을 어린이집에서 실제로 적용해보면서 보육교사의 역할을 직접 경험하는 것이다 첫째, 보육실습의 목적에 대해 적고 둘째, 보육실습생의 역할과 자세는 어떠해야 하는지 셋째, 실습의 경험이 향후 본인의 진로결정에 영향을 미칠 것인지에 대해 자신의 생각을 서론, 본론, 결론의 형식으로 논리적으로 서술해보세요
해당 정보 및 게시물의 저작권과 기타 법적 책임은 자료 등록자에게 있습니다. 위 정보 및 게시물 내용의 불법적 이용,무단 전재·배포는 금지되어 있습니다. 저작권침해, 명예훼손 등 분쟁요소 발견 시 고객센터에 신고해 주시기 바랍니다.













 분야
분야

