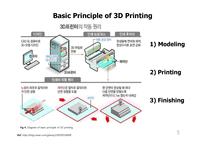
Basic Principle of 3D Printing
General Process of 3D printing
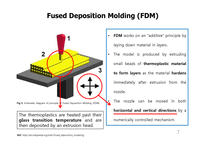
FDM - Fused Deposition Molding
SLA – Stereolithography
SLS - Selective Laser Sintering
FDM - Fused Deposition Molding
FDM works on an "additive" principle by laying down material in layers.
The model is produced by extruding small beads of thermoplastic material to form layers as the material hardens immediately after extrusion from the nozzle.
The nozzle can be moved in both horizontal and vertical directions by a numerically controlled mechanism.
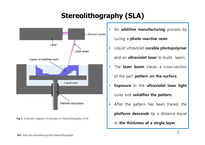
SLA - Stereolithography
An additive manufacturing process by curing a photo-reactive resin
Liquid ultraviolet curable photopolymer and an ultraviolet laser to build layers
The laser beam traces a cross-section of the part pattern on the surface.
Exposure to the ultraviolet laser light cures and solidifies the pattern.
After the pattern has been traced, the platform descends by a distance equal to the thickness of a single layer.
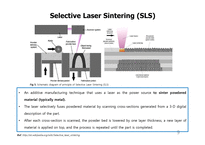
SLS - Selective Laser Sintering
An additive manufacturing technique that uses a laser as the power source to sinter powdered material (typically metal).
The laser selectively fuses powdered material by scanning cross-sections generated from a 3-D digital description of the part.
After each cross-section is scanned, the powder bed is lowered by one layer thickness, a new layer of material is applied on top, and the process is repeated until the part is completed.






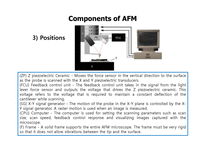

 분야
분야


