Ⅱ. A brief Outline of MDS
Ⅲ. Data
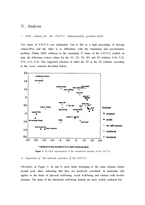
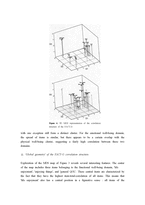
Ⅳ. Analysis
Ⅴ. Discussion
Ⅵ. Conclusion
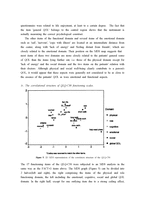
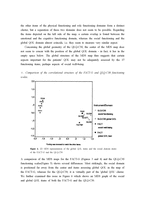
The goal of Multivariate statistical analysis(MSA) is dimension reduction of data. Especially, visualization of data is very important. In various methods of MSA, Multidimensional scaling(MDS) is introduced and discussed as a graphical method to complement conventional descriptive and confirmatory methods in validation and analysis of QOL data. The use of MDS is illustrated in an example based on a study of 300 cancer survivors who completed the functional assessment of cancer therapy-general(FACT-G) and the EORTC core quality of life questionnaire(QLQ-C30).
One characteristic of QOL instruments is their large number of items, their length usually ranges between 20 and 100 items, so interpreting output data is a little difficult. Consequently, in order to use such instruments appropriately in quantitative research, some sensible form of data reduction is necessary, i.e., condensation of the total information contained in the complete set of items to a fairly small set of composite variables reflecting the most important features of the instrument.
In this paper, various statistical techniques, both descriptive(exploratory) and analytical(confirmatory), are at hand to deal with this issue. Such data reduction methods are needed not only by those developing new assessment instruments, but also by those involved in translations or other modifications of existing instruments or engaged in methodological research, e.g. in a comparative analysis of several different QOL instruments.








 분야
분야


