Purpose of Experiment
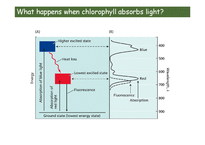
What happens when chlorophyll absorbs light?
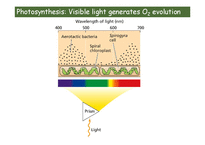
Photosynthesis: Visible light generates O2 evolution
Emerson and Arnold (1932) measured chl. molecules
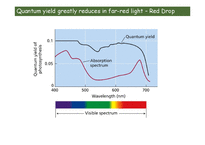
Quantum yield greatly reduces in far-red light – Red Drop
Both red and far-red light enhance photosynthesis
사실 명반응은 두 개의 광계에서 일어난다 (Z scheme)
광합성은 엽록체에서 일어난다.
Transfer of electrons are carried out vectorially
Plastoquinones are electron carriers in PSII
2 protons enter thylakoid when electron is transferred to PSI
Some herbicides kills weeds by blocking photosynthetic electron flow
If proton gradient is enough, ATP is synthesized even in the dark
The Hill Reaction
실험과정
HILL REACTION
6CO2 + 12H2O →> C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2
광합성은 명반응과 CO2 고정 반응으로 일어난다.
명반응에서 H2O는 빛에 의해 분해되어 전자(e-), H+와 O2가 발생하고, 전자는 엽록체의 thylakoid 막 안팎에 존재하는 전자 전달자들로 전달되어 NADP를 환원시킨다.
Chloroplast 분리
Hill 반응을 통한 광합성의 심층 이해
(DCPIP가 무색의 DCPIP-H2로 환원)
제초제 DCMU의 활성 메커니즘



















 분야
분야


