Spinodal Decomposition
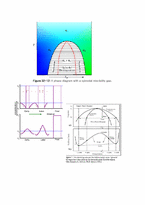
In thermodynamics, the binodal, also known as the coexistence curve or binodal curve, denotes the condition at which two distinct phases may coexist. Equivalently, it is the boundary between the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for the system to be fully mixed and the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for it to phase separate[1]. In general, the binodal is defined by the condition at which the chemical potential of all solution components is equal in each phase. The extremum of a binodal curve in temperature coincides with the spinodal curve and is known as a critical point.
Spinodal Decomposition
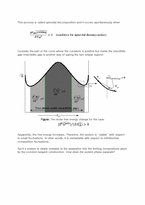
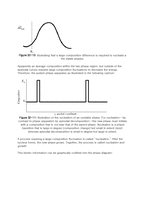
For those cases in which the molar free energy of mixing has regions of negative curvature (as in the example of the regular solution model), the mechanism by which the system decomposes into its equilibrium phases is different than the mechanism when the curvature is positive. This distinction between mechanisms when the curvature is negative (called the spinodal decomposition mechanism) when the curvature is positive (called the nucleation and growth mechanism) is important for kinetics. It will be useful to discuss the spinodal mechanism in the context of free energy curves.







 분야
분야


