A Study on the Liability for drone accidents
< 목 차 >
I. 서 설
II. 드론 보험에 대한 검토
Ⅲ. 드론사고에 대한 법적 구제방안 검토
Ⅳ. EU에서 드론의 민사법적 책임에 대한 검토
Ⅴ. 결 론
■ 국문요약 ■
무인 항공기(Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, UAV)를 뜻하는 드론(drone)은 최근 항공사업법 개정으로 공공용 드론에 대해 보험 가입이 의무화 되었다. 드론분야 선제적 규제혁파 로드맵에 따라 2025년 이후 발전단계 3단계에 이르면 자율비행이 가능해지고 드론 택시를 비롯하여 레저 드론이 인구밀집지역 비가시권 영역에서도 운행할 예정이어서 이에 대한 제도의 구비가 요구된다. 그러나 현행 민사법적 책임은 피해자가 가해자의 귀책사유를 입증하여야 하고 정식재판에 의할 경우 피해구제의 효율성이 떨어지는 문제가 있고 현재 운용되고 있는 드론 사고에 대한 영업배상책임 보험도 적용제외 되는 사유가 지나치게 많아 효율적인 구제가 이루어지지 못하고 있는 것이 현실이다. 피해자의 입증책임 부담을 완화하고 효율적인 피해구제를 위하여 No-Fault 보험제도의 도입 및 드론 사고조사위원회를 비롯한 ADR의 활용을 통하여 피해를 신속하게 구제하고 보험적용영역을 확대하면서 보험연계증권(ILS)의 발행을 통하여 보험회사가 분산된 포트폴리오를 보유하도록 하는 것이 바람직하다. 드론의 운행상 안전을 제고하기 위하여 사이버보험의 도입과 보험금의 효율적 운용을 위한 보험금청구권 신탁제도의 도입을 적극적으로 검토하여야 한다. 자율비행과 관련한 운행자의 위치정보와 개인 신상정보를 비롯한 동승자의 개인정보가 해킹으로 유출될 가능성에 대비하여 데이터 3법의 시행에 따라 운행과정에서 수집한 개인정보를 삭제하거나 대체하여 다른 정보와 결합하는 경우에도 특정 개인을 알아볼 수 없도록 익명처리하여 정보를 활용하는 방안이 마련되어야 한다.
국내논문
국회도서관, “비사업용 소형 드론 등록제 도입”, 2018.
김선이 · 최병철, “무인항공기 사고로 인한 운영자의 법적 책임 연구”, 전북대학교 법학연구소 법학연구 통권 제44집 2015.
김은경, “자율주행자동차 보험의 법적 과제”, 상사법연구 제38권 제4호, 2020.
김종복, “국내 상업용 민간 무인항공기 운용을 위한 법제화 고찰”, 한국항공우주 정책법학회지, 제28권 제1호, 한국항공우주법학회, 2013.
, “상법 항공운송편 제정의 필요성과 방향에 관한 고찰”, 법학연구 제11집 제1호, 인하대학교 법학연구소, 2008.
김주표, “무인항공기 드론 사고의 법적 책임과 보험제도”, 기업법연구 32(4), 2018.
김현우, “자율주행자동차에 대한 사이버보험의 필요성”, 법학연구 제20권 제3호, 2020.
박진서 외, “RPA 운영에 따른 사고발생대비 손해배상 법적체계 마련 제안”, 국토교통부, 2013.
박해선, “스마트사회와 민사책임”, 조선대학교, 법학논총, 제23집 제2호, 2016.
박훤일, “보험리스크의 증권화 - CAT 본드를 중심으로,” 고려대학교 법학연구원 고려법학 제44권, 2005.
소재현, “유럽연합 차원의 드론 운용규칙 제정 현황”, 월간교통, 2016.
이재훈, “데이터 3법 개정과 연구개발정보 활용을 위한 제언”, 한국과학기술기획평가원, 2020.
장훈, “유럽 드론법 성장과 규제 사이의 균형점”, 과학기술정책 제27권 제9호, 2017.
최순진 · 민귀옥, “자율주행자동차의 상용화에 따른 보험사기 대처방안에 대한 연구”, 가천법학 제11권 제4호, 2018.
한국민사법학회, “인공지능 사회를 대비한 민사법적 과제 연구”, 법무부 연구용역 과제 보고서, 2017.
홍준호 · 강주영, “정보주체 보호를 위한 사이버보험 의무 가입 필요성에 관한 연구”, 원광법학 제35권 제1호, 2019.
해외논문
Chopra Samir & Laurence White, “Artificial Agents and the Contracting Problem: A Solution via an Agency Analysis”, University of Illinois Journal of Law, Technology & Policy, 2009.
European Parliament, “Artificial Intelligence and civil law: liability rules for drones”, 2018.
Gunther, “EuropaischeRegelungen im Bereich Robotik -alles noch Science Fiction?”, DB 2017.
Kevin W. Williams, “Human Factors Implications of Unmanned Aircraft Accidents: Flight-Control Problems”, FAA, 2006.
Laurie R Blank, Cyberwar versus Cyber Attack : The Role of Rhetoric in the Application of Law to Activities in Cyberspace, in: Cyberwar, Jens David Ohlin/Kevin Gvern/Claire Finkelsten(ed.), 2015.
Lohmann, “Roboter als Wundertuten -eine zivilrechtliche Haftungsanalyse”, Aktuelle juristische Praxis: AJP/PJA 2/2017.
Abstract
A Study on the Liability for drone accidents
Drone, which means Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), has recently been revised in the Aviation Business Act, which has made it mandatory to purchase insurance for public drones. In accordance with the roadmap for preemptive regulatory reform in the drone field, after 2025, when the development stage reaches the third stage, autonomous flight will be possible, and leisure drones, including drone taxis, will be operated in the non-visible area of densely populated areas, and thus a system for this is required. However, the current civil legal liability is that the victim must prove the cause attributable to the perpetrator, and if it is a formal trial, there is a problem that the effectiveness of the damage relief is inferior, and the reason why the operating liability insurance for drone accidents currently in operation is also excluded. The reality is that there are not many effective relief measures. In order to ease the burden of proof of victims and to effectively relieve damages, the No-Fault Insurance System is introduced and the Drone Accident Investigation Committee and other ADRs are used to promptly relieve damage and expand the scope of insurance coverage, while insurance-linked securities (ILS) It is desirable to allow insurance companies to have a diversified portfolio through issuance of In order to improve the safety of drone operation, the introduction of cyber insurance and the introduction of a claim-right trust system for efficient management of insurance money should be actively considered. In preparation for the possibility that the personal information of the passenger, including the drivers location information and personal information related to autonomous flight, may be leaked due to hacking, the personal information collected in the driving process is deleted or replaced according to the enforcement of the Data 3 Act and combined with other information. Even in the case of doing so, there should be a plan to use the information by making it anonymous so that a specific individual cannot be recognized.
The European Aviation Safety Administration regulates a remotely controlled aircraft system (RPAS) in which pilots remotely control aircraft without boarding the vehicle. Regarding civil liability for each EU country, it is reported that the operator is responsible for an accident caused by the failure to secure the safety of the operation of the drone, and the operator has a strict certification responsibility. In relation to drone liability insurance, physical damages to self and passengers premised on the occupant are not included in the insurance content, but the insurance includes third-party liability, manager liability, and provision of collateral for damage to accessories. In calculating the damage related to the accident caused by the operation of the drone, the risk management method of minimizing the risk caused by the operation of the drone and allowing the person who can overcome the negative effects to take responsibility for the drone is used to relieve the victim and make a reasonable It is necessary to actively consider its use as an insurance method that can seek a solution.
Key words: Drone Insurance, Unmanne















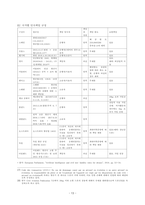






 분야
분야


